What does gout mean?
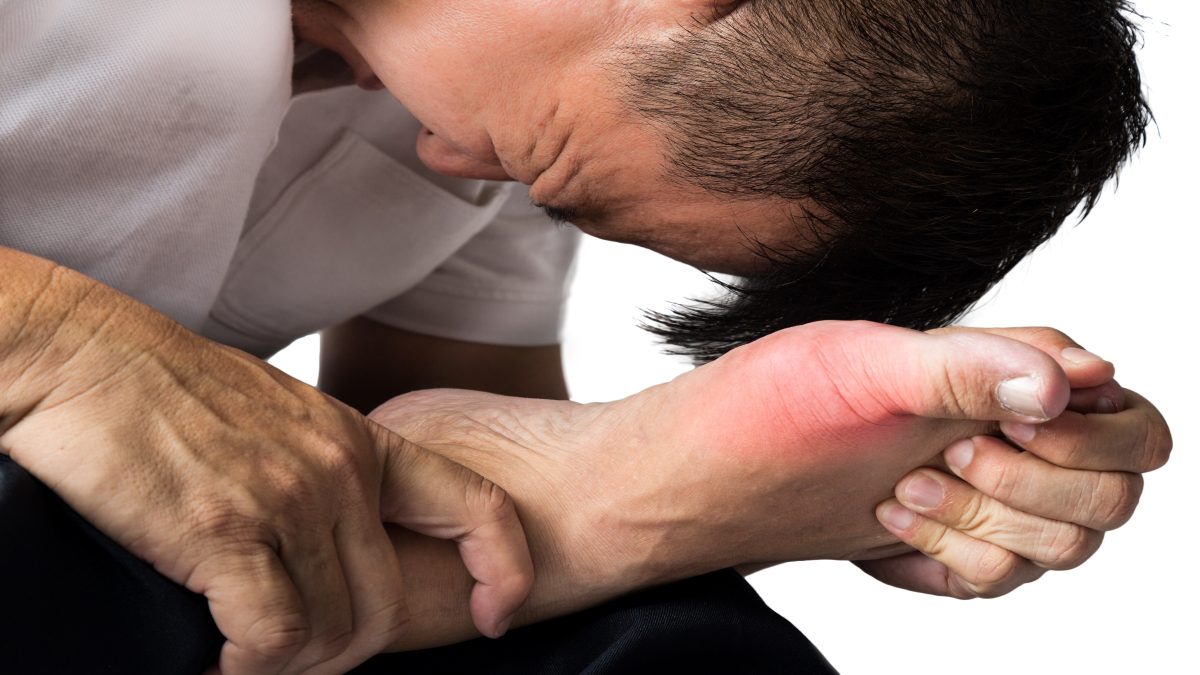
A gout is a form of arthritis that causes the sudden onset of painful inflammation and redness in the affected joints because of crystal deposits. At one time, it was called “the disease of kings” because it was thought to be associated with overeating wine and rich foods, but the truth is, anyone can develop gout. Gout in the big toe is the most common. However, this condition occasionally affects other joints as well, such as the elbows, wrists, ankles, knees, feet, and hands. Sometimes it affects tendons and soft tissue. Gout usually affects only one joint at a time, however in some cases, it becomes chronic, and over time affects multiple joints.
Gout attack
It typically occurs suddenly. A gout attack is often causing you to be awake in the middle of the night with a feeling that your big toe is burning. You will find the affected joint swollen and hot and so tender that even the weight of a bedsheet can feel unbearable.
Prevalence
In America alone, over 3 million people are affected by gout. The disease and complications associated with it occur more frequently in men, people with kidney disease, and women following menopause. There is a strong link between gout and the following medical conditions:
- diabetes
- obesity
- hypertension (high blood pressure)
- hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol and high triglycerides)
Gout risks
If you have high uric acid levels in your body, you are more likely to develop gout. Factors that increase your body’s level of uric acid include:
- Alcohol use: Excessive use of alcohol increases your risk of developing gout. This typically means more than one drink per day for women and more than two drinks per day for men.
- Other medical conditions: Having other certain medical conditions increases your risk of also developing gout. These include high blood pressure that hasn’t been treated, diabetes, arteriosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries), and hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol).
- Certain medications: Taking certain medications can increase uric acid levels in your blood. These include thiazide diuretics (prescription drugs used to treat high blood pressure), low dose aspirin, and anti-rejection medications (drugs prescribed for those who have had transplant surgery).
- A family history of gout: Gout tends to run in some families, so you may be more likely to develop gout if someone else in your family has or had the disease.
- Age and sex: Due to their increased uric acid levels, more men than women are affected by gout. Following menopause, women’s uric acid levels rise, so women then become more at risk for the disease. Men typically develop gout earlier than women, in their 40’s and 50’s. Gout is rare in children.
Causes of gout
A build-up of urate crystals in a joint typically causes gout. These are tiny crystals that are very sharp and shaped like a needle. When they accumulate in a joint, they cause severe pain and inflammation. Urate crystals form when there is a too high level of uric acid (a regular waste product) in the blood.
Increased blood levels of uric acid can happen because the body over-produces uric acid or because the kidneys cannot filter it out of the blood well enough. In addition, certain foods and beverages cause levels of uric acid to rise. Some of these are organ meats, shellfish, mushrooms, and excessive amounts of alcohol.
Click Here to read about Symptoms.















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.