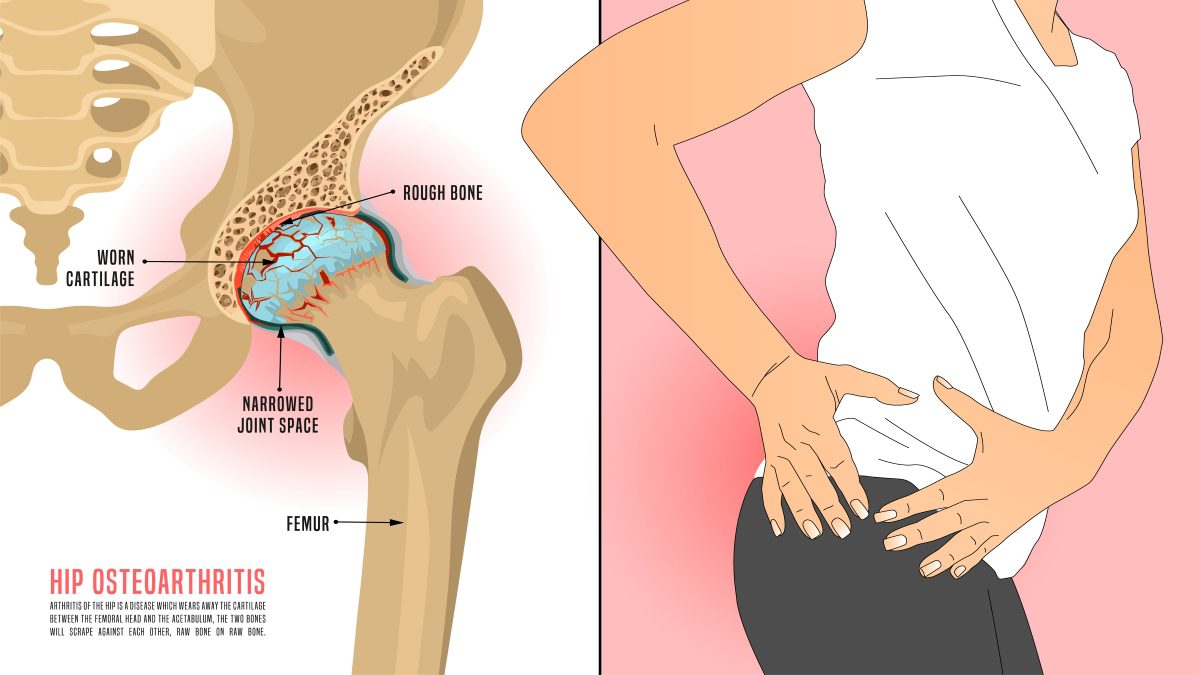
Treatment of hip osteoarthritis
The changes that occur in the hip joint caused by hip osteoarthritis can’t be reversed, but the progression of the disease can be slowed. The goal of most treatments, like strengthening muscles and weight loss, is to reduce the stress on the joints of the hips. In addition, other hip osteoarthritis treatments, including injections, surgery, and medications, are sometimes used in patients who suffer from moderate to severe symptoms of hip osteoarthritis.
Conservative Treatments for Hip Osteoarthritis
PHYSICAL THERAPY
Physical therapy may be recommended to provide one or more of the following treatments:
- A specific and individualized program of exercises that stretches and strengthens the hip muscles. This will help provide improved support for the hip joint and ease some of the stress to the joint that is being caused by hip osteoarthritis.
- Work with a person to develop a program of specific exercises focused on improving balance and gait. Supportive or assistive devices might also be introduced, like a cane.
- Manual therapy: Physical therapists sometimes use this technique to help increase joint movement in a patient who experiences hip osteoarthritis.
ACTIVITY MODIFICATION
Exercise is essential in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis, but certain kinds of exercise and activities irritate the joints in the hip and should be avoided. Golf is one example. It requires a twisting motion in the hip. Other activities involving high force on the joint, like jogging, should also be avoided by people with hip osteoarthritis. Exercises that are less stressful for the hip joint are swimming, yoga or cycling.
PERIODIC REST
Achiness is not uncommon when joints that are stiff first start to loosen after prolonged rest, like early in the morning or when exercise is first begun. But if you feel severe pain, don’t try to “work through it.” Pain is your body’s way of telling you that your joint needs to rest.
WEIGHT LOSS
The hip joint supports a tremendous amount of weight. If you gain only ten extra pounds, this can mean an additional 60 pounds of weight is then placed on your hip joint each time you take a single step. Losing and maintaining a healthy weight is one of the best and simplest ways to relieve the painful symptoms of hip osteoarthritis.
Medications for Hip Osteoarthritis Treatment
Doctors sometimes recommend hip osteoarthritis medications to help relieve the symptoms or to slow down the progression of the condition. You and your physician should talk about how medications relate to your medical history, lifestyle, and how severe your pain is. Other factors to consider are how medicines will interact with other drugs you are taking and the potential for adverse side effects.
- Pain relievers: Also sometimes called analgesics, these drugs help manage pain. Acetaminophen is an example of a medication that helps to relieve pain, with few side effects, but it does not control inflammation.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: These are also known as NSAIDs. In addition to relieving pain associated with hip osteoarthritis, these medications also reduce swelling and inflammation. They include drugs like ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, and Cox-2 inhibitors. These drugs can cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as bleeding, in some patients. Some of these medications are available over-the-counter, and others require a doctor’s prescription.
- Topical analgesics: These medications are applied to the skin on the hip. They contain various ingredients like anti-inflammatories or counter-irritants, like eucalyptus or wintergreen. These distract the brain from pain by stimulating the nerve endings and can be used along with oral medications for hip osteoarthritis.
Supplements to treat hip osteoarthritis
Chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate: These substances are found naturally in the cartilage of the body. Some patients with hip osteoarthritis were found in studies to benefit from the use of these supplements, but more research is needed to understand the exact role they play in the disease.
Steroid and hyaluronic acid injections
Injections are sometimes used to treat severe pain caused by hip osteoarthritis:
Steroid injections: Corticosteroids are powerful hormones that are anti-inflammatories. These help in reducing the swelling caused by hip osteoarthritis, which helps relieve pain and stiffness in the joint.
Hyaluronic acid injections: This medication provides lubrication in the joint of the hip, helping to relieve the pain and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis.
Not everyone who has hip osteoarthritis finds injections to be helpful. Furthermore, if the injections are effective, the beneficial effect is only temporary and lasts approximately six months to one year.
The goal of injections for hip osteoarthritis is usually to provide relief from pain so the patient can begin physical therapy. If a treatment program begins to strengthen the hip muscles, by the time the benefit of the injections has worn off, the patient’s symptoms have decreased due to exercise. Injections may also be considered for patients with hip osteoarthritis who cannot tolerate oral medications.
Other conservative treatments for hip osteoarthritis
SUPPORTIVE DEVICES
Certain orthopedic devices are sometimes used to help reduce pressure or to stabilize the hip. These may include:
- Shoe inserts: These can help cushion and provide relief from pressure that occurs to the hip joint during walking
- A cane: The use of a cane is sometimes recommended to help provide stability when walking
- A walker: To provide even more stability in severe cases of hip osteoarthritis, the use of a walker may be recommended, especially to reduce the risk of a fall if a person’s balance is affected by pain or hip instability.
- Other devices: There are many other supportive devices available to help with daily tasks. These reduce the need to bend at the hips. Examples include devices to help put on socks, reachers, and grabbers, and long-handled shoehorns.
COPING TECHNIQUES
To help cope with hip osteoarthritis pain, patients often use techniques like relaxation, biofeedback, visual imagery, hypnosis, or distraction. For many people, these interventions, used with a positive mental outlook focusing on what they can do, rather than on the negative role hip osteoarthritis plays in their life, has a significant impact on relieving hip pain.
Surgery for Hip Osteoarthritis Treatment
Surgery may be recommended when hip osteoarthritis pain is disabling, and no relief is obtained with conservative treatments. Surgical treatment for hip osteoarthritis may include:
- Osteotomy: This is rarely used to treat hip osteoarthritis. It involves the cutting of either the joint socket or the thighbone and the realignment of the joint to relieve pressure.
- Hip resurfacing: This is a type of hip replacement surgery that involves replacing the cartilage in the socket and the damaged bone with an artificial shell. The head of the thighbone is not replaced. It is capped instead with a smooth covering made of surgical steel.
- Total hip replacement: In this procedure for hip osteoarthritis, the surgeon replaces the entire hip joint with an artificial joint made of plastic, metal, or ceramic material.
Complications
The most frequent complications of hip osteoarthritis surgery include:
- Infections
- Blood clots
- Excessive bleeding
- Dislocation of the hip joint
- Damage to the arteries or blood vessels
- The difference in leg length
Your surgeon will explain the possible complications before you have surgery, and you will be allowed to ask questions.
Recovery
After any procedure for hip osteoarthritis, there is a recovery period. The time it takes to recover depends on the type of procedure performed and the severity of the patient’s condition. Many times, physical therapy is recommended after surgery to help the patient recover their strength and mobility. Following surgery, a walker, crutches, or a cane are often needed to allow healing to take place. Most of the time, surgery is effective for relieving the pain of hip osteoarthritis, and patients are able to eventually resume their normal tasks.














Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.