Ingrown toenail treatment
Physicians treat ingrown toenails in different ways, depending on how severe they are and whether they have occurred frequently in the same toe. Treatments used by doctors for ingrown toenails include surgical and non-surgical methods.
Lifting the nail
If the nail is slightly ingrown and does not have signs of infection, the doctor might lift up the edge of the ingrown toenail and place a piece of a splint, dental floss, or cotton underneath of it. This will help the ingrown nail separate from the skin and encourage it to grow out above the edge of the skin. This treatment is followed by daily foot soaks at home, after which the patient replaces the splinting material.
Surgery for ingrown toenail treatment
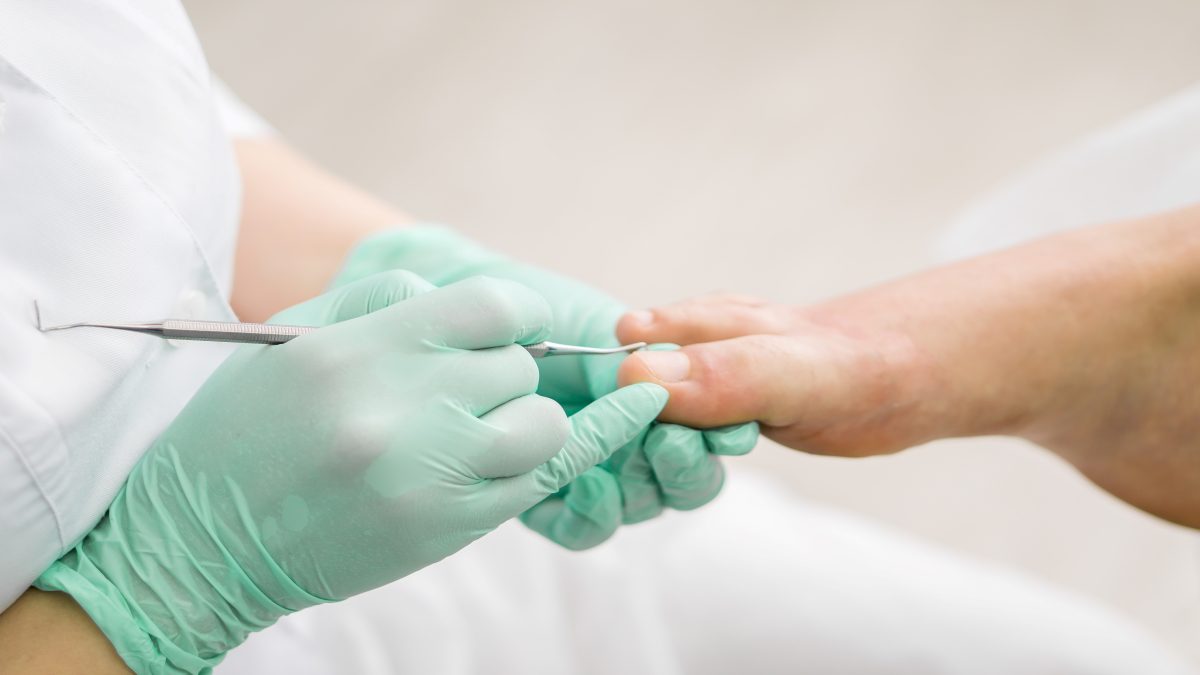
In some cases, when the patient experiences recurrent ingrown toenails or has another condition such as diabetes that may lead to complications, ingrown toenail surgery is recommended. The surgery involves partial or complete removal of the ingrown toenail.
- Partially removing the ingrown toenail. If the ingrown toenail is more severe, the ingrown portion might be removed or trimmed. This may require numbing the toe with an anesthetic prior to the procedure.
- Removing the nail and tissue. If an ingrown toenail repeatedly occurs on the same toe, a physician may recommend the removal of part of the nail and the nail bed, which is the tissue under the nail. This can help keep the part of the nail that was removed from growing back.
If the ingrown toenail is infected or is at risk for infection, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed.
Prevention of ingrown toenail
Ingrown toenails can be prevented by:
- Trimming the toenails straight across. Don’t trim your toenails in a curve that matches the shape of your toe. If you have toenails trimmed by a pedicurist, tell them to trim the nails straight across. If you have diabetes or another condition that impairs circulation to the feet, have a podiatrist trim your nails every four to six weeks.
- Keep nails at a moderate length. To prevent ingrown toenails, keep the nails about even with the ends of the toes. When nails are too short, pressure from the shoes can cause the nail to grow down into soft tissue.
- Wear shoes that fit. When shoes are too tight or pinch, they can press toenails into the soft tissue. If you have diabetes or other nerve conditions, you might not be able to tell if your shoes are pinching your feet. If you have diabetes or nerve impairment, get help from a shoe specialist when purchasing shoes to ensure you get a proper fit to prevent ingrown toenails and other foot problems.
- Wear protective footwear. If your job places you at risk of a toe injury, wear shoes or boots with steel-toes. Injuring your toes increases your risk of ingrown toenails.
- Check your feet. People who have diabetes need to inspect their feet every day for evidence of foot or toe problems like ingrown toenails.
Useful Advices
In many cases, ingrown toenails can be treated at home. Here are some suggestions:
- Soak feet in warm water. Soaking feet and toes help to relieve tenderness and decrease inflammation. Soak ingrown toenails for about 20 minutes four times daily.
- Splint the toenail with dental floss or cotton: After you soak your ingrown toenail, put a clean “splint” made of dental floss or a small piece of cotton under the edge that has grown in. This will coax the nail to grow above the edge of the skin.
- Apply antibiotic ointment. Bandage the ingrown toenail after applying a small amount of antibiotic cream or ointment to the area.
- Choose proper footwear. If it’s practical, wear sandals or open-toed shoes until the toe is less painful.
- Take pain medication. Pain relievers like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen are available over-the-counter and can help relieve the pain of an ingrown toenail.
Outcome & Complications
If an ingrown toenail is untreated, it can cause infection in the bone of the toe, leading to severe complications.
Complications of ingrown toenails can especially be severe in the presence of diabetes. Diabetes can restrict blood flow, and it also can damage the nerves in the feet. This can cause even minor foot injuries and sores, like ingrown toenails, to not heal well and become infected. In addition, open wounds may need surgery to prevent tissue death.














Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.