Musculoskeletal pain can cause significant discomfort. Moreover, if left unmanaged, it can lead to some complications. Therefore, it is essential to diagnose musculoskeletal pain in time and assign a proper treatment.
Musculoskeletal pain diagnosis
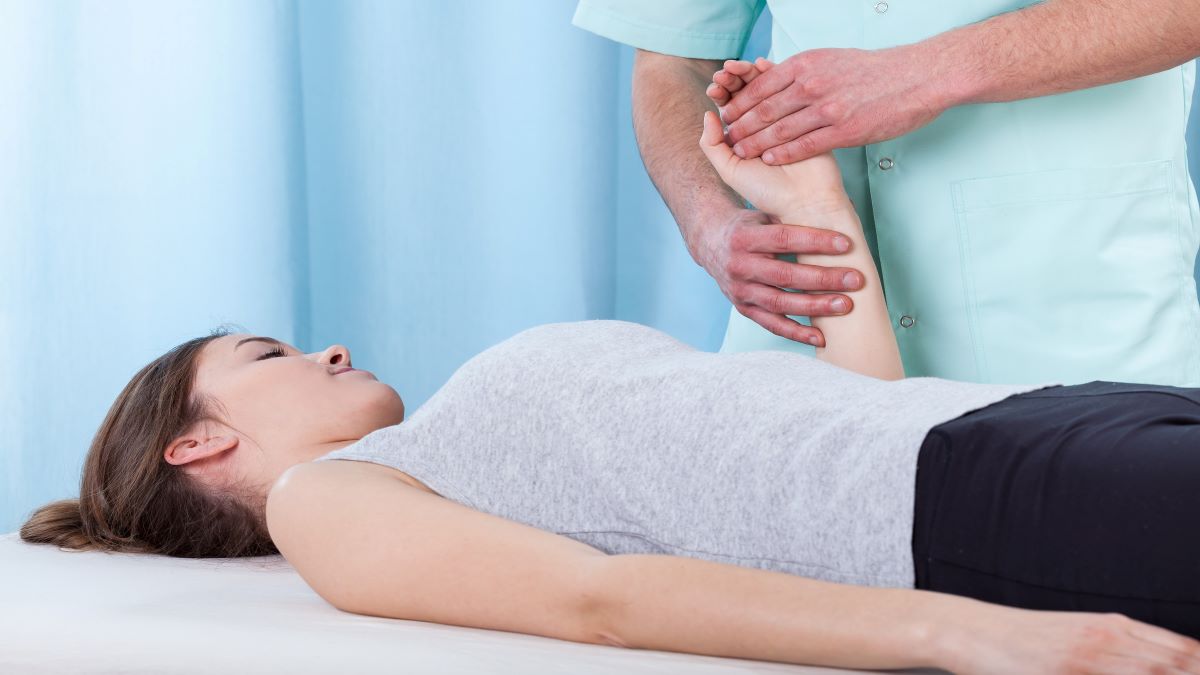
The healthcare provider performs a physical examination to diagnose musculoskeletal pain, evaluating for the presence or absence of signs related to specific conditions or disorders.
Assessment of bones
Sometimes, areas affected by musculoskeletal disorders are not painful or are not misshapen. For example, a compression fracture of the spine due to osteoporosis or a stress fracture caused by overuse may not produce an abnormal change in alignment. Still, it can result in musculoskeletal pain. If the doctor notices unusual bumps or hard knots in the bone, a tumor might be suspected. High fever with musculoskeletal pain might indicate bone infection (osteomyelitis).
Assessment of muscles
To diagnose the cause of musculoskeletal pain, a doctor will also ask about and check the strength of the muscles in the painful area. In addition, the healthcare provider will check for muscle tone and tenderness. Muscle tone indicates the tension in the muscle when it is not in use. Involuntary muscle movements, tremors, or twitches sometimes indicate nerve disorders instead of a muscle problem.
Wasting away muscle tissue or atrophy can result from the lack of use or nerve or muscle damage. An overgrowth of muscle tissue, called hypertrophy, is usually due to repetitive stress, like exercise or weight lifting. Hypertrophy can also occur when one muscle overworks to compensate for weakness in other muscles affected by disease or disuse. In addition, some musculoskeletal disorders may result from the growth of abnormal tissue, which replaces the normal one.
Assessment of Joints
To determine the reason for musculoskeletal pain, your healthcare provider may check how far you can move your joints. The limited ability to move the joints can result from weakness, stiffness, swelling, or pain. There may also be scarring present in or around a joint that limits its mobility.
Additionally, the healthcare provider will examine how far the patient’s joints will move with assistance. The doctor may also check for joint stability or the presence of abnormal fluid in a joint.
Other tests
The doctor can often diagnose the cause of musculoskeletal pain based on your history and symptoms and the information obtained in the physical exam. However, your doctor may recommend tests, imaging studies, or diagnostic procedures to assist in making or confirming a final diagnosis.
- Laboratory tests. They may include:
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
- Rheumatoid factor
- The healthcare provider may request other blood tests to diagnose people suspected of having lupus and identify those at risk for other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Tests of the nerves and muscles. Nerve conduction studies help evaluate if the nerves which supply the muscles are working correctly. They can help determine whether a problem exists in the muscles, nervous system, or neuromuscular junction.
- Imaging studies. It may include:
- X-rays
- Arthrography
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasonography
- Bone scanning
- Arthrocentesis
- Arthroscopy
Musculoskeletal pain treatment
The treatment of musculoskeletal pain may involve different approaches. Most of the time, a combination of several treatments is used. They may include:
- Limiting movement in the affected area
- Applications of cold or heat
- Gentle exercise or stretching
- Medications
- Surgery
Limiting movement
The first treatment for musculoskeletal pain and disorders is to limit movement in the affected area and avoid performing the activities that resulted in pain if an injury occurred. For example, if musculoskeletal pain is related to work, this might require work restrictions.
The patient may benefit from splints. They help immobilize or restrict movement in a painful or injured joint or support a joint. However, placing you in a splint to manage musculoskeletal pain doesn’t mean that you can resume the activity that caused your injury. If you go back to such activity, you could damage other joints that will work for the splinted one.
Application of cold or heat
Applying cold or heat as a treatment for musculoskeletal injuries can be pain-relieving. It may also help speed up the healing of injured tissues. Applications of cold can assist in decreasing pain and inflammation. It is often recommended for pain accompanied by swelling, redness, and increased warmth, especially immediately following an injury.
Heat may be advantageous as a treatment for musculoskeletal pain. It stimulates blood flow to the painful area, which helps eliminate lactic acid. However, you shouldn’t apply heat to swollen areas unless your doctor has recommended you do this.
Exercise and stretching
Healthcare providers sometimes recommend gentle exercises and stretching to treat musculoskeletal pain because they help get rid of muscle tension and increase circulation to the area. However, people with musculoskeletal pain or disorders should talk to their doctor before beginning a stretching or exercise program. It can increase pain or worsen an existing problem if not performed correctly.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications help relieve mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain. These medicines are known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs, and they reduce pain and inflammation.
When musculoskeletal pain is more severe, the doctor may prescribe stronger NSAIDs or other types of pain pills. In addition, your healthcare provider may recommend different types of medications, such as muscle relaxants.
Surgery
Depending on the reason for musculoskeletal pain, if other treatment approaches fail to provide relief, surgery may be necessary.
How to prevent musculoskeletal pain?
The risk for musculoskeletal pain and disorders increases as you grow older, so prevention is essential. You can decrease the risk by practicing healthy lifestyle habits early in life. Prevention of musculoskeletal pain includes:
- Practice regular strengthening and stretching exercises
- Don’t smoke or use tobacco products
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet
- Maintain good posture
- Learn and practice correct lifting techniques















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.