Spinal nerves are nerves that extend from the right and left sides of the vertebral column. Their primary function is to carry information about the body to and from the brain through the spinal cord. In humans, spinal nerves are organized in 31 pairs divided into five segments corresponding to the parts of the spine. Therefore, there are eight pairs of spinal nerves in the cervical segment, twelve pairs in the thoracic segment, five pairs in the lumbar segment, five pairs in the sacral segment, and one pair in the coccygeal segment.
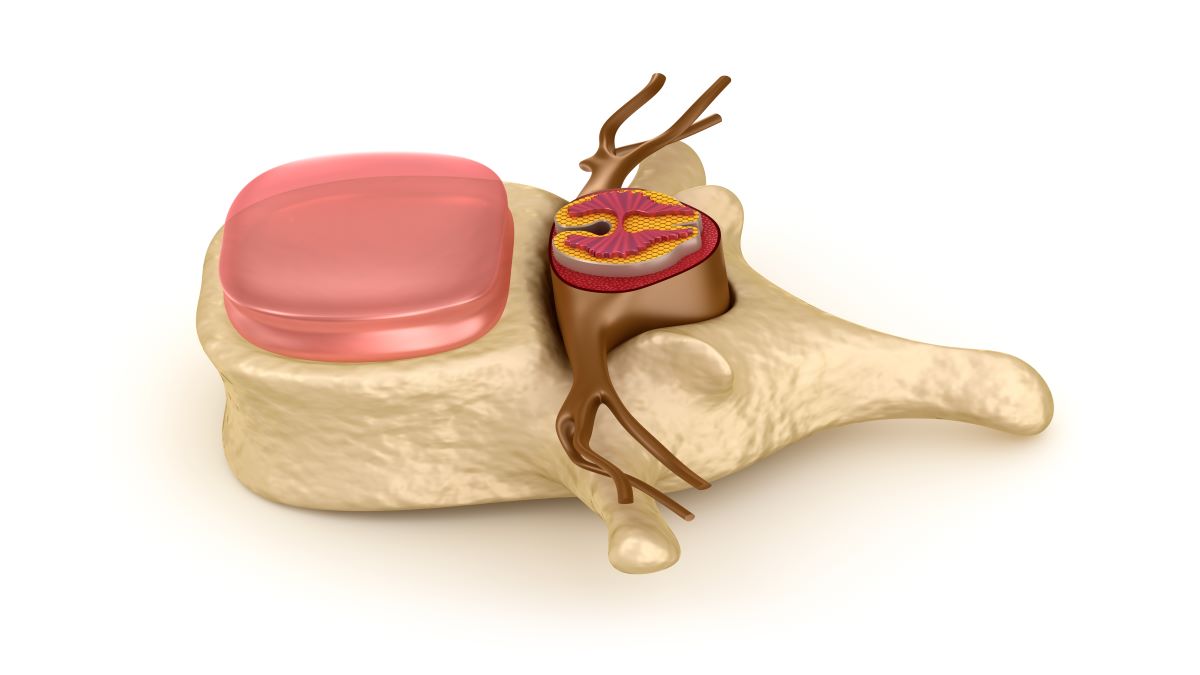
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves meaning that they carry sensory (to the brain), motor (to the body) and autonomic (both directions) information. Fibres composing each nerve originate in either the dorsal or ventral root of the spinal cord. Spinal nerves enter and exit the vertebral column through the space between two adjacent vertebrates called the intervertebral foramen. After leaving the spine, these nerves split into two main branches that transmit information from and to the different body parts. More specifically, one of them carries signals from and to the front part of the body. The second goes to the back of the trunk and limbs.
Cervical nerves
The eight spinal nerves of the cervical segment of the spinal cord go to the three muscles of the neck. They also form networks of different cervical nerves from which fibres supply the back of the head and some neck muscles, chest, shoulders, arms, forearms, and hands.
Thoracic nerves
As all of the spinal nerves do, thoracic nerves divide into two branches. The frontal division carries information about abdominal muscles, the skin of the hip and the back of the arm, and the ribs. The posterior division contains the medial branch of the spinal nerves. The upper six thoracic nerves go to the upper and back parts of the neck. They also supply the back muscle, which plays a significant role in the stability of the spine. The medial branch of the lower six thoracic nerves ends up in some muscles of the back.
Lumbar nerves
The frontal branch of the lumbar nerves supplies the muscles of the lower back. A medial branch is also present on the dorsal division of the lumbar nerves and goes to the back muscle. The side branches of this division supply the set of muscles responsible for the vertebral column extension.
Sacral nerves
There are two holes in the sacrum where the sacral nerves exit the vertebral column. Coccygeal nerves form associations with each other and with some lumbar and coccygeal nerves and supply the tight, hip, leg, and foot areas. In addition, some of the sacral nerves go to some parts of the intestine, urinary bladder and sex organs.
Coccygeal nerve
One pair of coccygeal nerve supplies the skin area near the coccyx bone.
The optimal work of different pairs of spinal nerves is crucial for the normal functioning of the body. Disturbances in the activity of the spinal nerve can lead to defective or lost sensation, impaired reflexes and muscle weakness.
Source Wikipedia















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.