If you suffer an ACL injury, it means the anterior cruciate ligament located inside of your knee joint has torn or ruptured. The anterior cruciate ligament is commonly known as the ACL. An ACL injury is most likely when a person is participating in a sport that requires frequent and sudden stops with changes in direction, like volleyball, tennis, soccer, and basketball.
Some people feel a popping sensation or may even hear a “popping” noise when an ACL injury occurs. Other symptoms include swelling, pain, and instability in the knee, making it difficult to bear weight and walk.
If an anterior cruciate ligament injury is severe, treatment may involve surgery to replace the ACL. Rehabilitative therapy and exercises designed to help the patient regain their strength and stability in the injured joint often follow the surgery. A training program can also decrease the risk of an anterior cruciate ligament injury.
What is an ACL?
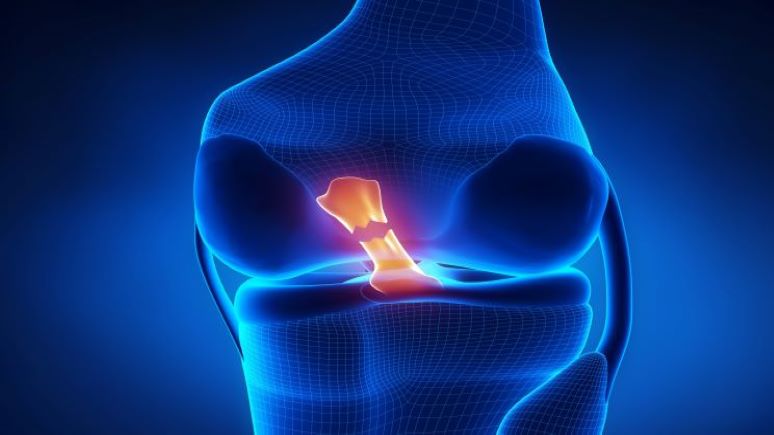
The anterior cruciate ligament connects to the end of your thigh bone or femur in the back of your knee. It passes through the knee in a diagonal direction to connect with the shin bone. Another ligament, the posterior cruciate ligament, passes across the knee in the opposite direction. These two ligaments form a “cross” shape. It is why they are called “cruciate” ligaments.
Your ACL prevents your shin bone, or tibia, from moving in front of your knee. Likewise, your posterior cruciate ligament keeps the tibia from moving backward. These two ligaments are critically important in providing stability to the knee joint, especially when you are involved in activities requiring sudden changes in direction.
Prevalence
- In the United States, an estimated 200,000 injuries related to the ACL occur each year. Approximately 95,000 of these are actual ruptures. The highest anterior cruciate ligament injury incidence is found in people participating in high-risk sports, including soccer, skiing, football, and basketball.
- The prevalence of ACL injury is greater in females than in males. The rate is up to 9.7 times greater in females than males.
- Anterior cruciate ligament injury cases are common in men, as more men participate in sports. Still, women have a greater risk of being injured.
- Because of their active lifestyle and greater participation in high-risk sports, ACL injuries are most prevalent in people from 15 to 45 years old.
ACL injury causes
An anterior cruciate ligament injury can occur in many different ways:
- Suddenly coming to a stop
- Rapidly changing direction
- Suddenly slowing down when running
- Incorrectly landing from a jump
- A collision or direct contact, for example, a football tackle
Research has shown that ACL injury is more common in females than males who participate in particular sports activities. It may be because of differences in muscular strength, physical condition, and neuromuscular control. Another cause of an ACL injury that is more likely to occur in women is differences in the ligament properties due to the effects of the hormone estrogen. In addition, differences in the alignment of the leg and pelvis or loosening in the ligaments may cause an ACL injury.
ACL injury risk factors
Some factors can increase a person’s risk of an ACL injury. They include:
- Being female
- Participating in particular sports
- Using artificial turf for games
- Incorrect movement patterns (for example, bending the knees inward during a squat)
- Poorly fitting footwear
- Lack of conditioning
- Using sports equipment that is in an impaired condition
Click Here to read about Symptoms.















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.