Arthritis is a disorder that involves different tissues inside the joints. Your joints locate where two or more bones of the body come together. Sometimes, arthritis occurs due to inflammation resulting from a chronic condition or because of acute inflammation in a joint and the tissues surrounding it. Traumatic damage to a joint can also lead to arthritic changes in it. In addition, there is a possibility that hereditary and environmental factors can also increase the risk of arthritis.
In arthritis, wear and tear damage causes erosion of the joint cartilage and the joint itself. Cartilage is the material lining the joints. It is smooth and provides protection from friction, and allows smooth movement between the bones. When the cartilage wears down, the soft tissues in that area can also be affected. These tissues include ligaments, tendons, nerves, blood vessels and muscles, skin, fatty tissue, and the membranes that support, surround or connect other organs or bodily structures. These arthritic changes caused by a breakdown in cartilage can often be seen on X-rays.
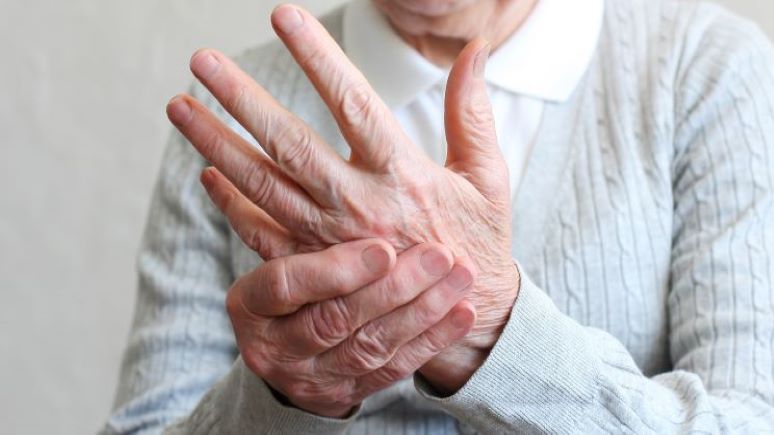
In many people, arthritis causes pain and a loss of mobility. In addition, the joints may become deformed and stiff. Any of the body’s joints can become arthritic, but arthritis in the hands and the wrist is common. What’s more, arthritis in the hand can cause deformities of the fingers, leading to increased pain and loss of functioning.
Types of arthritis in hands
There are over 100 different types of arthritis. Still, the most commonly found forms of arthritis in hands are either rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
Prevalence
Almost every person, especially older people, is affected by osteoarthritis. Destruction of the joints is revealed on X-rays in approximately 60% of people over 60 years. It is seen in over 80% of people who are over 75 years old. Osteoarthritis is more common in women than in men, and the condition typically begins earlier in life in females.
Rheumatoid arthritis is not as common as osteoarthritis. It only affects approximately 1% of adults and typically begins when a person is between the ages of 20 and 40 years old. In addition, rheumatoid arthritis is three times more common in women than in men.
Causes of arthritis in hands
Disease
When arthritis occurs as a degenerative disease process, due to wear and tear damage that happens over time, the cartilage wears away slowly. It means that the symptoms of the disease usually come about gradually.
Osteoarthritis generally affects older individuals. Another name for osteoarthritis is “wear and tear” arthritis. It is because it causes the wearing away of cartilage in the joints. In some joints of the body, this happens in a predictable pattern.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects the synovium or lining of the joints. It causes this part of the joint to swell due to inflammation, causing stiffness and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect many different joints in the body, and it is a chronic illness. Typically, rheumatoid arthritis affects the same joints of the body on both the right and left sides. It usually starts in the small joints of the toes, feet, and fingers.
Trauma
Broken bones or fractures especially breaks in the bones that affect or damage the joint, can lead to arthritis. Even when they receive the proper treatment, joint dislocations are more likely to become arthritic than joints that have never been injured.
Arthritis in hands risk factors
Some factors may be important in the development of osteoarthritis. For example, joint alignment and stability, which are mechanical considerations, play a role in how forces are distributed across a joint, so these can impact the health of the joint. In addition, substances like biochemicals within the joint’s cartilage may play a part in abnormal changes that occur over time in the joint tissue.
Several factors may place a person at increased risk for the development of osteoarthritis. These include:
- Traumatic injury to a joint
- Infection in the joint
- Age
- Damage that occurs as a result of overuse of the joint
- Genetic factors
It is not well understood what role heredity plays in the development of osteoarthritis. Usually, people who have inherited the condition are affected by osteoarthritis at a younger age.
Click Here to read about Symptoms.















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.