Symptoms of gout
Attacks of gout almost always come on suddenly and without warning, and they often occur at night. Signs and symptoms of gout include:
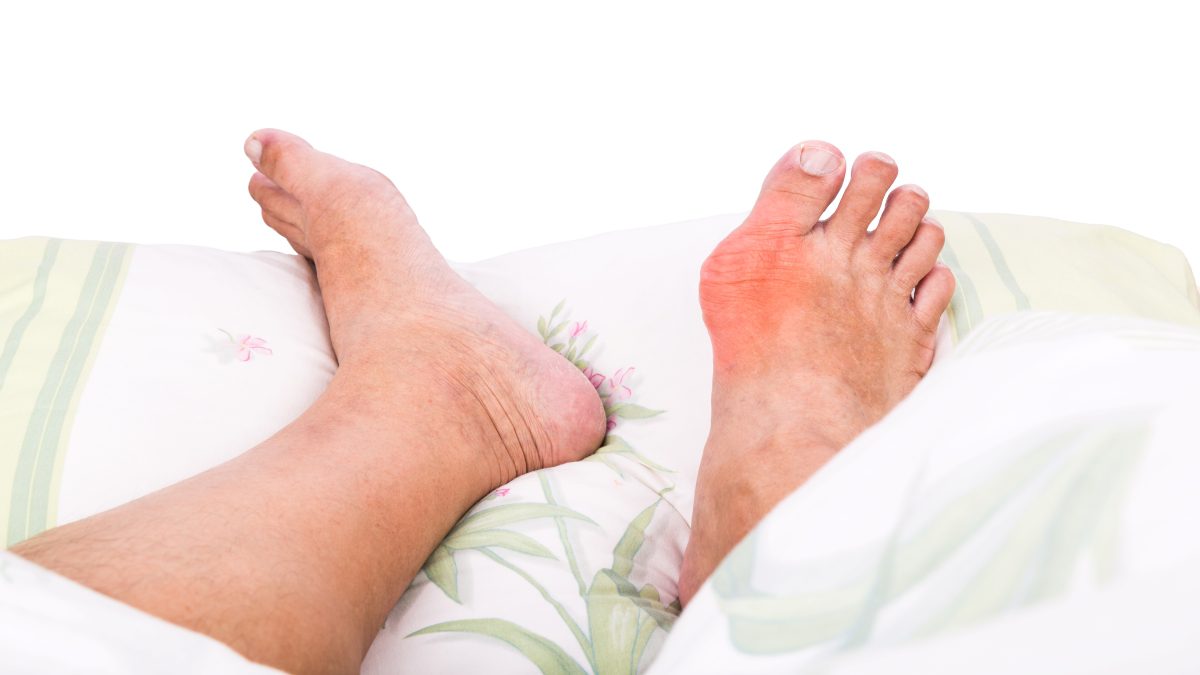
- Severe joint pain: Gout is often most painful when the attack begins for the first 12 to 24 hours. The most commonly affected site is the big toe, but gout can develop in the hands and wrists, knees, ankles, or feet.
- Lingering pain: After the first 12 to 24 hours, the most severe pain usually subsides, but some aching discomfort and tenderness may persist for several days to a few weeks. Future episodes may last longer and involve more areas (joints).
- Redness and inflammation: The joints that are affected become painful, swollen, and red.
When to see a doctor
Untreated gout can cause increased pain and can even lead to joint damage. If you experience gout symptoms, such as sudden and severe pain in a joint, notify your doctor.
Seek medical care right away if you have a fever and a joint feels hot to the touch and is swollen, red and painful because these can be signs of infection.
Gout diagnosis
Other forms of arthritis share some of the same signs and symptoms of gout, so an accurate diagnosis is important. Your physician may suspect a gout diagnosis if you have a history of severe pain and swelling in one or two joints that last several days, followed by periods when you are free of symptoms.
In addition to obtaining your medical history and performing a physical examination, your physician will also look for the presence of urate crystals that help to diagnose gout. A needle may be used to obtain fluid from the joint that is affected. The fluid will then be studied under a microscope to check for the presence of the crystals.
In cases of chronic or advanced gout, hard lumps called tophi form under the skin. These lumps are deposits of uric acid and are also a sign of gout diagnosis.
Blood tests to diagnose gout can be unreliable. Increased uric acid levels sometimes appear in people who have never had gout, and at times, people who are experiencing a severe episode of gout will have an unusually low blood level of uric acid.
X-rays sometimes reveal joint damage caused by chronic gout.
Pathological changes
Gout can lead to other, more severe health problems such as:
- Recurrent gout: Some people who have one gout episode never have signs or symptoms of the condition again. Others may continue to experience flare-ups repeatedly.
- Advanced gout: Some people who have untreated or chronic gout develop deposits of urate crystals under their skin. These deposits form knots or nodules called tophi. Tophi can become tender and swollen during attacks of gout. They typically develop on the hands and fingers, elbows or feet, or on the back of the ankle.
- Kidney stones: These can be caused by the collection of urate crystals in the urinary tract.
Click Here to read about Treatment.















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.