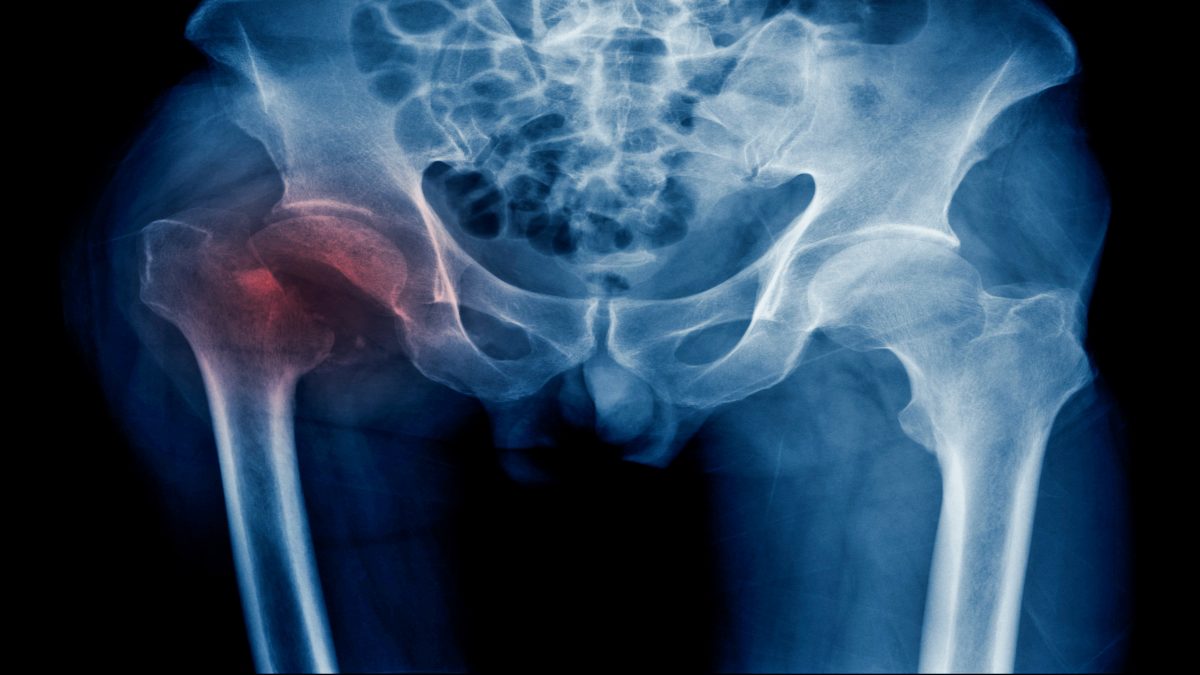
Treatment of hip fracture
Treatment of a hip fracture typically involves a combination of pain medications, surgery, and physical therapy.
Surgery for hip fracture treatment
The surgical procedure performed depends on the type and severity of the hip fracture, the patient’s age, and other medical or health conditions. Options for hip fracture surgery include:
- Internal repair with the use of screws. Surgical screws are placed in the bone to hold it in place while the hip fracture heals. In some cases, a surgical plate is inserted, running down the femur, and the screw is attached to this.
- Partial hip replacement. If the ends of the femur are damaged or out of position, the surgeon might replace the neck and head of the broken bone with an artificial replacement.
- Total hip replacement. In this procedure, the upper part of the femur, in addition to the socket, is removed and replaced with prostheses. Total hip replacements are sometimes done when hips are worn out due to arthritis and are causing pain and difficult movement, even if they are not fractured.
A partial or total hip replacement might be recommended if circulation to the hip joint was injured when the hip fracture occurred. This kind of injury, more likely to occur with fractures of the femoral neck, often results in poor healing.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation begins for most patients the day after surgery. Exercises start with gentle motion and strengthening. Some people are discharged home from the hospital, and other patients go to an extended care facility for continued rehabilitation after hospitalization.
Occupational therapists and physical therapists help patients recover more quickly from surgery for a hip fracture. They assist with exercises, help with assistive devices, teach energy conservative and pain management techniques and help patients resume independence in tasks of daily living.
Hip fracture medication
Approximately one-fifth of patients who suffer one hip fracture will fracture a hip again within twenty-four months. Medications called bisphosphonates may help reduce the chances of a repeat fractured hip.
Bisphosphonates are taken by mouth most of the time, but side effects can make them hard to tolerate. These side effects include inflammation of the esophagus and acid reflux. For this reason, doctors sometimes suggest taking these drugs directly into a vein (intravenously).
Bisphosphonates generally are not prescribed for people who have kidney disorders. In rare cases, long-term use of bisphosphonates may cause swelling and pain in the jaw, problems with vision, or atypical hip fractures.
Prevention of hip fracture
To help prevent hip fractures, start early. Making healthy choices related to lifestyle early in adulthood helps build peak bone mass and can reduce the risk of osteoporosis later. Healthy choices also can reduce the risk of falls and improve overall health.
To help reduce the risk of falls and to keep your bones healthy, follow these suggestions:
- Get enough vitamin D and calcium. In general, people who are 50 years or older should get 600 IU (international units) of vitamin D and 1,200 milligrams of calcium per day. This helps ensure bones remain as strong as possible to prevent osteoporosis and avoid hip fracture.
- Exercise to improve balance and strengthen bones. Weight-bearing exercise, like walking, helps to increase overall strength, which decreases the risk of falls. It also helps maintain peak bone density longer. Balance tends to worsen with age, so balance training can reduce the risk of hip fracture by decreasing the risk of falling.
- Avoid excessive alcohol intake and tobacco in all forms. Alcohol and tobacco use reduces bone density. Overuse of alcohol can also negatively impact balance and increase the chance of falls.
- Assess your environment. Look for and remove hazards such as throw rugs, electrical cords in pathways, and furniture that clutters walkways and causes trips and falls. All rooms, hallways, and entryways should be well-lit.
- Check your vision. Get your eyes checked at least every two years. People who have diabetes or an eye disorder need an eye exam more frequently.
- Monitor medications. Feeling dizzy, off-balance, or weak are side effects caused by many drugs. These can be responsible for hip fractures because they increase the risk of falls. Ask your doctor about the potential side effects of any medications that you are taking.
- Change positions slowly. Standing up too quickly may cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness and falls. Change positions slowly, and make sure you have your balance before starting to walk. This can help prevent hip fractures by reducing the chances of a fall.
- Use a walker or cane if needed. Ask your physician or physical therapist if a cane or walker might help you if your gait is unsteady.
Outcome & Complications
Hip fractures have the potential to reduce a person’s independence. They can even shorten a person’s life. About 50% of people who suffer a hip fracture never regain their independence.
Potential complications of the immobility related to a hip fracture include:
- Blood clots in the lungs or in the legs
- Pressure ulcers (Bedsores)
- Pneumonia
- Infections of the urinary tract
- Loss of strength and muscle mass, which increases the risk of future falls and hip fractures
People who have had a hip fracture are at an increased risk of decreased bone density, which increases their risk of suffering another fracture.














Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.