Symptoms of arthritis
Typically, the joints are affected by arthritis. Depending on the form of the condition that is present, signs and symptoms of arthritis can include:
- Pain in the affected joint(s)
- Swelling in the affected joint(s)
- Stiffness in the affected joint(s)
- Decreased mobility in the affected joint(s)
- Redness in the affected joint(s)
Arthritis risks
Exactly arthritis causes are not known, but certain factors make it more likely the condition will develop. Arthritis risk factors include:
- Family history: Certain forms of arthritis have a tendency to occur in families. This means your risk of developing arthritis may be greater if your parents or a brother or sister have the condition.
- Age: Growing older increases the risk of several forms of arthritis. These include gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis.
- Gender: Your sex can make you more susceptible to certain types of arthritis. Men, more often than women, develop gout. Women are at elevated risk of rheumatoid arthritis than men.
- A history of joint injury: Arthritis is more likely to eventually develop in a joint that has been previously injured.
- Obesity: Being overweight causes excess stress on the body’s joints, especially on weight-bearing joints like the hips and the knees. This increases the risk of arthritis.
Causes of arthritis
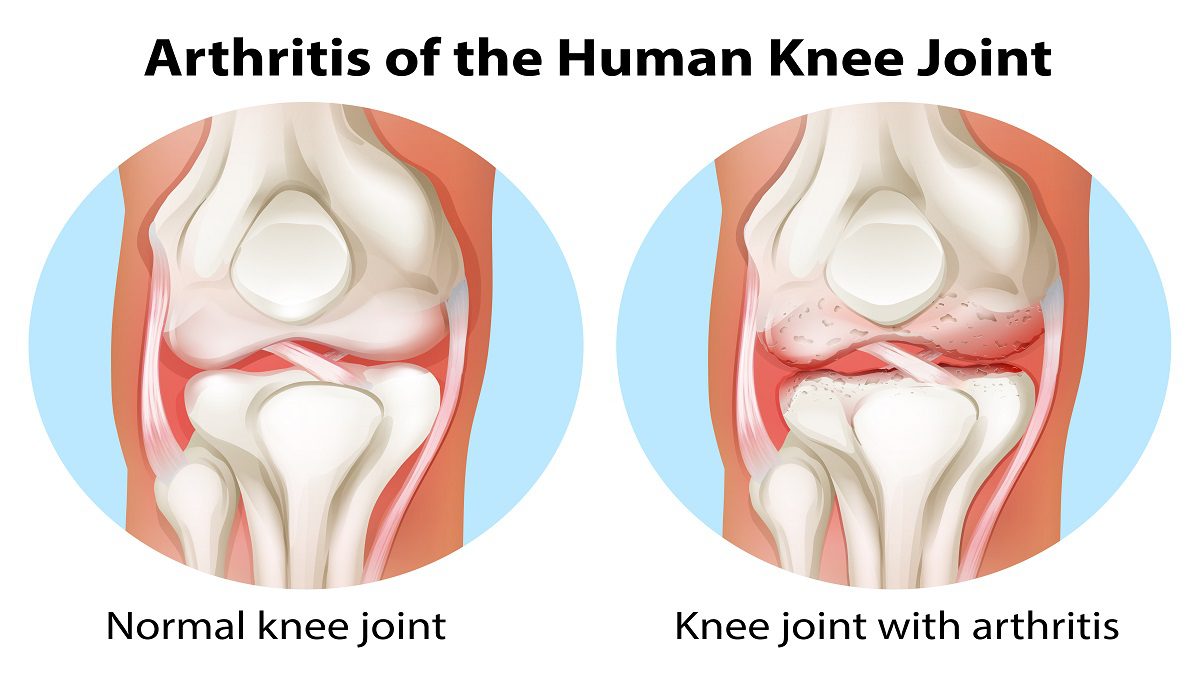
- OSTEOARTHRITIS. Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that first affects the lining of a joint. This lining is made up of smooth cartilage material. Without this smooth cartilage material, movement in the joint is impaired, causing the stiffness and pain of arthritis. As the cartilage that lines the joint becomes thin, other tissues are allowed to move against each other. This leads to inflammation, and bony spurs start to develop. Bony spurs are also known as osteophytes. In osteoarthritis, the ends of the bones in the joints rub together due to the loss of the protective cartilage.
- RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. The inflammation and pain of rheumatoid arthritis are caused by an autoimmune disorder that causes the body’s immunity to attack the affected joints, causing inflammation and damage. Rather than the joint cartilage, the first area of the joint to be affected in this type of arthritis is the covering surrounding the joint. This is known as the synovium. The inflammation can then spread, which causes even more inflammation and can cause disfigurement of the joint. The joint cartilage and the bones can then break down.
- JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is sometimes called juvenile idiopathic arthritis. It can cause persistent pain in the joints, stiffness, and swelling. Sometimes, children have these symptoms for just a few months. In other children, the symptoms persist for the remainder of their lives. Some forms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis cause severe complications, including problems with the eyes and problems with the child’s growth.
Click Here to read about Treatment.















Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.